

Up: Long period variable stars:
3 The statistical method
In this paper the Luri-Mennessier (LM) statistical method, described in
Luri et al. (1996), is used to analyze the sample of LPV stars. The
method
has been specifically designed to exploit the HIPPARCOS data and thus is
suitable for our purposes. This method has already given fruitful
results, in
particular for Barium stars (Mennessier et al. 1997c), Ap-Bp stars
(Gomez
et al. 1998) and the LMC distance modulus (Luri et al. 1998).
The use of appropriate statistical methods for the exploitation of
the HIPPARCOS astrometric data is crucial in order to obtain correct
results.
Otherwise the values obtained can be affected by strong biases and the
precision of the data will not be fully used. A discussion on the
correct use of HIPPARCOS data and recommendations on analysis techniques
can be found in Brown et al. (1997).
The LM method used in this paper is especially appropriate for use with
the
HIPPARCOS data. We refer to Luri et al. (1996) for a detailed
description, and only briefly summarize here some of its main features.
First of all, the stellar population from which the sample is
extracted is assumed to be composed of several distinct groups.
These
groups can differ in kinematics, luminosity or spatial distribution
and
its number is a priori not known. Therefore, using a sample
extracted from
this base population and taking into account the selection
criteria
used to create it, the LM method:
- determines the number of significant discriminating groups and
the percentage of each of them in the population;
- produces, for each group, unbiased estimates
of the parameters of the model used to describe it, i.e.:
- a Schwarzschild ellipsoid velocity distribution characterized
by
(
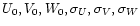 ).
U0, V0 and W0 point towards
the galactic center, the galactic rotation, and the north
galactic pole, respectively;
).
U0, V0 and W0 point towards
the galactic center, the galactic rotation, and the north
galactic pole, respectively;
- an exponential distribution of the number of stars in the
direction perpendicular to the galactic plane, with a scale
height Z0;
- a normal distribution of the absolute magnitude in
the bandpass of the used observed magnitudes characterized by
the
parameters M0 and
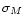 .
.
The results of this first step for our LPVs sample are given in Sect.
4.
The minimum input data needed by the LM method are the measured
positions,
proper motions and apparent magnitudes of the stars, but it can also use
the parallaxes and radial velocities if available. The method takes into
account the selection effects of the sample, the observational errors,
the
galactic rotation and the interstellar absorption.
In a second step, once the groups are identified and parametrized, the
method:
- computes for each star of the sample,
the a posteriori probability that the star
belongs to a given group;
- uses a Bayesian rule to assign each star to a group;
- uses a statistical estimator to obtain estimations of individual
distances and luminosities for each star.
This second step is presented in Sect. 5 where the
representativity of our sample with respect to the kinematic and
photometric properties of the population is also discussed.


Up: Long period variable stars:
Copyright ESO 2001
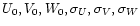 ).
U0, V0 and W0 point towards
the galactic center, the galactic rotation, and the north
galactic pole, respectively;
).
U0, V0 and W0 point towards
the galactic center, the galactic rotation, and the north
galactic pole, respectively;
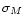 .
.