| Issue |
A&A
Volume 521, October 2010
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A52 | |
| Number of page(s) | 4 | |
| Section | Cosmology (including clusters of galaxies) | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201014602 | |
| Published online | 20 October 2010 | |
Research Note
Brans-Dicke model constrained from the Big Bang nucleosynthesis and magnitude redshift relations of supernovae
1
Department of Physics, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, 812-8581, Japan e-mail: [berni;riou;hashimoto]@phys.kyushu-u.ac.jp
2
Department of Physics, Kumamoto University, Kumamoto, 860-8555, Japan e-mail: arai@sci.kumamoto-u.ac.jp
Received:
31
March
2010
Accepted:
12
July
2010
We investigated the Brans-Dicke model with a variable cosmological term (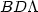 ) with the coupling constant ω = 104. We constrained the parameters inherent in this model
from a comparison between the Big Bang nucleosynthesis and the observed abundances. Furthermore, we studied the magnitude redshift
(m–z) relations for the BDΛ with and without another constant cosmological term in a flat universe. Observational data of type Ia supernovae (SNIa) are used in the redshift range of
0.01 < z < 2. We found that our model with an energy density of the constant cosmological term of 0.7 can explain the SNIa
observations, though the model parameters are insensitive to the m–z relation.
) with the coupling constant ω = 104. We constrained the parameters inherent in this model
from a comparison between the Big Bang nucleosynthesis and the observed abundances. Furthermore, we studied the magnitude redshift
(m–z) relations for the BDΛ with and without another constant cosmological term in a flat universe. Observational data of type Ia supernovae (SNIa) are used in the redshift range of
0.01 < z < 2. We found that our model with an energy density of the constant cosmological term of 0.7 can explain the SNIa
observations, though the model parameters are insensitive to the m–z relation.
Key words: primordial nucleosynthesis / dark energy / early Universe / cosmology: observations / dark matter / cosmology: theory
© ESO, 2010
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


